- Write the function \(\texttt{int READDIM()}\) that reads and returns a strictly positive integer less than 50;
- Write the function \(\texttt{void READARRAY(int Arr[], int N)}\) that reads \(\texttt{N}\) positive integers of the array \(\texttt{Arr}\);
- Write the function \(\texttt{void SORT(int Arr[], int N)}\) that sorts in increasing order the array \(\texttt{Arr}\);
- Write the function \(\texttt{int Kth(int Arr[], int N, int k)}\) that returns
- the \(\texttt{k}\)th element of the array \(\texttt{Arr}\) if it exists ;
- -1 if it doesn't;
- Using all the above written functions, write a \(\texttt{main}\) function that displays the k\(^{th}\) largest element in an array (maximum size 50) of positive integers.
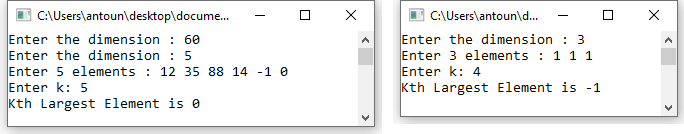
Running examples:
Difficulty level

This exercise is mostly suitable for students
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define SIZE 50
int READDIM()
{
int n;
do
{
printf("Enter the dimension : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
} while (n <=0 || n>SIZE);
return n;
}
void READARRAY(int Arr[], int dim)
{
int i;
printf("Enter %d elements : ", dim);
for (i = 0; i<dim; i++)
do {
scanf("%d", &Arr[i]);
} while (Arr[i] < 0);
}
void SORT(int Arr[], int dim)
{
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < dim; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < dim; j++) {
if (Arr[i] > Arr[j]) {
temp = Arr[i];
Arr[i] = Arr[j];
Arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int Kth(int Arr[], int dim, int k)
{
if(k>0 && k<=dim)
return Arr[k-1];
return -1;
}
void main()
{
int n, T[SIZE], k;
n = READDIM();
READARRAY(T, n);
SORT(T, n);
printf("Enter k: ");
scanf("%d", &k);
printf("Kth Largest Element is %d\n", Kth(T,n, n-k+1));
getch();
}
Back to the list of exercises
Looking for a more challenging exercise, try this one !!
 Width of binary trees - iterative version
Width of binary trees - iterative version