- Write a function that returns the value of the father of a given element in a binary tree of integers without repetition.
- Write a function that returns an array containing the values of all ancestors of a given element in a binary tree of integers without repetition ordered from the nearest to the farthest.
Example: the sorted ancestors of 3 in the following tree are: 2, 5, 10.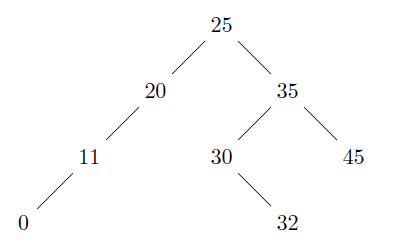
- Write a function that returns the value of the nearest common ancestor of two given elements in a binary tree of integers without repetition.
Example: the nearest common ancestor of 3 and 9 is 5.
Difficulty level

This exercise is mostly suitable for students
int father(Btree A, element e, element *p)
{
if (A==NULL || (A->left==NULL && A->right == NULL)) return 0;
if (A->left && A->left->data==e || A->right && A->right->data == e)
{
*p = A->data;
return 1;
}
if(father(A->left,e,p)) return 1;
return father(A->right,e,p);
}
void ancestors(Btree A, element e, element tab[],int *N)
{
element p;
*N=0;
while(father(A,e,&p))
{
tab[*N] = p;
e = p;
(*N)++;
}
}
int nearest_common_ancestor(Btree A, element e1, element e2, element *anc)
{
element tab1[100],tab2[100];
int N1,N2,i1,i2;
ancestors(A,e1,tab1,&N1);
ancestors(A,e2,tab2,&N2);
for (i1=0 ; i1<N1 ; i1++)
for (i2=0; i2<N2; i2++)
if (tab1[i1] == tab2[i2])
{
*anc = tab1[i1];
return 1;
}
return 0;
}Back to the list of exercises
Looking for a more challenging exercise, try this one !!
 Hashing using quadratic probing
Hashing using quadratic probing